What is Artificial Inttigence (AI) how it works in Real life
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science that aims to develop machines that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and natural language processing. The key idea behind AI is to simulate human intelligence in machines so that they can learn, reason, and solve problems like humans. In recent years, AI has gained a lot of attention and has become a hot topic in the technology industry. In this blog post, we will discuss how AI works, its applications, and the challenges it faces.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
There are two main types of AI: narrow or weak AI, and general or strong AI. Narrow or weak AI refers to AI systems that are designed to perform a specific task, such as facial recognition, language translation, or chess playing. These systems are typically trained on large datasets and use machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and make predictions. General or strong AI, on the other hand, refers to AI systems that can perform any intellectual task that a human can do. Such systems are still in the early stages of development and are considered to be a long-term goal of AI research.
How AI Works
The basic idea behind AI is to build machines that can learn from data and use that learning to make decisions. This involves the use of machine learning algorithms that can identify patterns and correlations in data and use that knowledge to make predictions. The three main types of machine learning are supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where an algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset, which means that the data has been labeled with the correct output. The algorithm learns from the labeled data to make predictions on new, unlabeled data. For example, if we want to build an algorithm that can recognize images of dogs and cats, we would train it on a dataset of labeled images where each image is labeled as either a dog or a cat. The algorithm would then learn to identify the features that distinguish dogs from cats and use that knowledge to make predictions on new, unlabeled images.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where an algorithm is trained on an unlabeled dataset. The algorithm learns from the data to identify patterns and correlations that can be used to cluster the data into groups or identify outliers. For example, if we want to analyze customer data to identify customer segments, we might use unsupervised learning to cluster customers based on their purchasing behavior.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an algorithm learns by trial and error. The algorithm receives feedback in the form of rewards or punishments based on its actions, and it uses that feedback to learn which actions are good and which are bad. For example, if we want to build an algorithm that can play a game, we might use reinforcement learning to train the algorithm to make good moves and avoid bad ones.
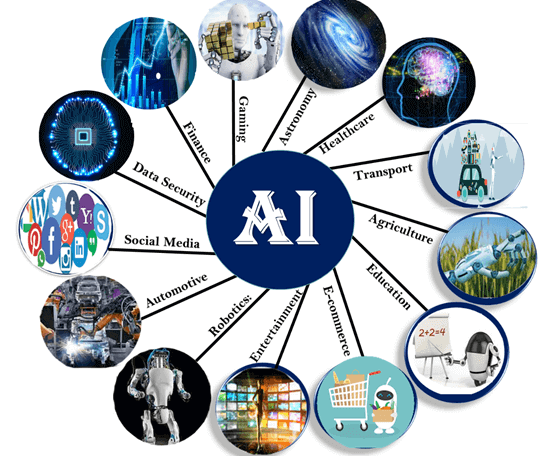
Applications of AI
AI has a wide range of applications in various fields, including healthcare, finance, education, transportation, and manufacturing. Here are some examples of how AI is being used in different industries.
Healthcare
AI is being used in healthcare to improve patient care, diagnose diseases, and develop new treatments. For example, AI algorithms are being used to analyze medical images to identify signs of cancer, to analyze patient data to predict which patients are at risk of developing a disease, and to develop personalized treatment plans based on a patient's genetic data.
Finance
AI is being used in finance to analyze data and make predictions about market trends, stock prices, and customer behavior. For example, AI algorithms are being used to analyze customer data to identify which customers are most likely to churn, to develop personalized investment strategies based on a
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most rapidly advancing and promising technologies of our time. It has the potential to revolutionize every industry, from healthcare to finance, and transportation to entertainment. AI can be defined as a field of computer science that enables machines to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision-making, and visual perception.
In this blog, we will dive deeper into the workings of AI, its various types, its advantages and disadvantages, and its potential impact on society.
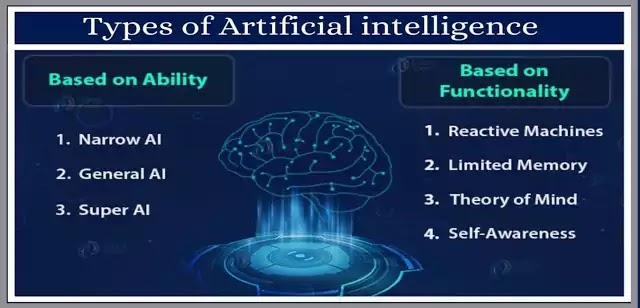
Types of AI
There are three types of AI: Narrow or Weak AI, General AI, and Super AI. Each of these types of AI has different levels of complexity, autonomy, and capabilities.
Narrow or Weak AI
Narrow or Weak AI is designed to perform specific tasks, such as playing chess or recommending products on an e-commerce website. It uses pre-defined rules and algorithms to complete its tasks and does not have the ability to learn and improve on its own. These systems are not truly intelligent but are simply following the instructions provided to them.
Examples of narrow AI include virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, recommendation systems used by e-commerce websites like Amazon, and speech recognition systems used by banks and insurance companies.
General AI
General AI, also known as strong AI or human-level AI, is designed to perform any intellectual task that a human can do. This type of AI would be able to learn and improve on its own and adapt to new situations without being explicitly programmed to do so. It is still a theoretical concept, and researchers are still working on developing a system that can mimic human intelligence.
Super AI
Super AI, also known as artificial superintelligence, is a hypothetical future AI system that would surpass human intelligence in all fields, including creativity, social skills, and emotional intelligence. Super AI would be capable of solving problems beyond human comprehension and could even develop new scientific theories and discoveries.
How AI Works
The workings of AI can be broken down into four stages: data input, processing, decision-making, and output.
Data Input
The first stage of the AI process is data input, which involves feeding data into the system. The data can be in various formats, such as text, images, audio, or video, and can come from different sources, such as sensors, databases, or the internet.
Processing
Once the data is input into the system, it undergoes processing, which involves analyzing the data to extract meaningful information. This is done using various techniques, such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing.
Machine learning involves training the system on a large dataset to learn patterns and relationships within the data. The system uses this information to make predictions or decisions based on new data. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks to analyze complex and unstructured data, such as images and audio. Natural language processing involves analyzing and understanding human language to enable the system to interact with humans in a more natural way.
Decision-Making
After processing, the system makes a decision based on the data it has analyzed. The decision can be a recommendation, a prediction, or an action. The system uses pre-defined rules and algorithms to make these decisions.
Output
Finally, the system produces an output based on its decision. The output can be in various formats, such as text, images, audio, or video, and can be used to take further action, such as controlling a robot or sending a response to a user.
Advantages of AI
Increased Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of AI is its ability to increase efficiency in various industries. AI can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex and





Nice content and explanation
ReplyDelete